พวกเราส่วนใหญ่ใช้ส่วนต่อประสานกราฟิกกับผู้ใช้ (GUI) เนื่องจากสะดวกกว่าการจำบรรทัดคำสั่งแบบเดิม แต่สิ่งหนึ่งที่แน่นอนก็คือ คุณไม่สามารถทำงานทุกอย่างใน GUI ของ Windows ได้ และนั่นคือเวลาที่พรอมต์คำสั่งสามารถให้บริการของคุณได้
อินเทอร์เฟซบรรทัดคำสั่งในตัวนี้สามารถสร้างผลลัพธ์ได้ทันทีโดยใช้คำสั่งง่ายๆ ด้วยทรัพยากรคอมพิวเตอร์ที่น้อยลง ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณไม่ต้องนำทางผ่านหน้าต่างต่างๆ เพียงเพื่อทำงานเดียวให้เสร็จ ด้วยโปรแกรมนี้ คุณสามารถใช้ฟังก์ชันการดูแลระบบขั้นสูงหรือแก้ไขปัญหาต่างๆ ของ Windows ได้ด้วยตัวคุณเอง!
ในบทความนี้ ฉันจะพูดถึง 50 คำสั่งที่คุณต้องรู้เพื่อใช้งาน Command Prompt แต่หากคุณค่อนข้างใหม่กับยูทิลิตี้นี้ เราขอแนะนำให้ตรวจสอบคู่มือสำหรับผู้เริ่มต้นก่อน
คำสั่งพื้นฐาน
ก่อนที่จะลงลึกถึงคำสั่งหลัก ผมจะเริ่มต้นด้วยคำสั่งพื้นฐาน ไม่ว่าคุณกำลังวางแผนที่จะใช้ Command Prompt อย่างกว้างขวางหรือเพียงเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ทั่วไป สิ่งเหล่านี้จะเป็นประโยชน์
CLS

คำสั่งนี้เป็นการล้างหน้าจอพรอมต์คำสั่ง หากคุณรู้สึกว่าต้องการเคลียร์พื้นที่ทำงานหลังจากใช้คำสั่งมากเกินไป สิ่งนี้จะมีประโยชน์อย่างมาก สิ่งที่คุณต้องทำคือพิมพ์ cls และกด Enter
Syntax: cls
Exit

หากคุณวางแผนที่จะปิดแอปพลิเคชันพรอมต์คำสั่ง คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องเลื่อนเคอร์เซอร์ เพื่อกดปุ่มปิด เพียงเรียกใช้คำสั่ง exit และโปรแกรมจะปิด
คุณยังสามารถใช้พารามิเตอร์/b เพื่อ ออกจากสคริปต์ชุดงานที่โหลด ด้วยวิธีนี้ หน้าต่างหลักยังคงเปิดอยู่และออกจากแบตช์ไฟล์เท่านั้น อย่างไรก็ตาม หากคุณใช้พารามิเตอร์นอกสคริปต์ พารามิเตอร์จะปิดแอป CMD
ไวยากรณ์: exit/b [รหัสข้อผิดพลาด]
โดยที่รหัสข้อผิดพลาดระบุค่าบางอย่าง จำนวน
ความช่วยเหลือ
คำสั่งนี้เข้ามา สะดวกถ้าคุณเจอคำสั่งใด ๆ และต้องการทราบการทำงานของมัน ซึ่งจะให้ไวยากรณ์พร้อมกับพารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ (สวิตช์)
หากคุณเพียงแค่เรียกใช้ help มันจะแสดงรายการคำสั่งทั่วไปที่ใช้ใน Command Prompt
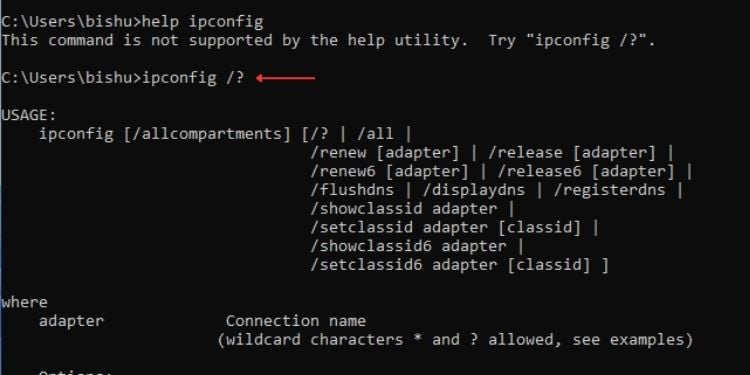
Syntax: help

อย่างไรก็ตาม ไม่ใช่ทุกคำสั่งที่รองรับยูทิลิตี้นี้ ในกรณีนั้น คุณสามารถใช้เครื่องหมาย/? พารามิเตอร์และควรใช้ได้กับทุกคำสั่ง
ไวยากรณ์:/?

CD หรือ CHDIR

เพียงแค่หมายถึง’เปลี่ยนไดเรกทอรี’และตามชื่อที่แนะนำ เปลี่ยนคุณจากไดเร็กทอรีปัจจุบันตามเส้นทางที่ระบุ
หากคุณเรียกใช้งาน cd มันก็จะแสดงชื่อไดเร็กทอรีปัจจุบันของคุณ ดังนั้น สิ่งสำคัญคือต้องเรียนรู้พารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ พร้อมกับฟังก์ชันและไวยากรณ์:
หมายเหตุ: คำสั่ง chdir และ cd ดำเนินการเหมือนกัน ดังนั้น คุณสามารถเปลี่ยนไดเร็กทอรีโดยใช้ตัวเลือกที่ต้องการ
คลิป
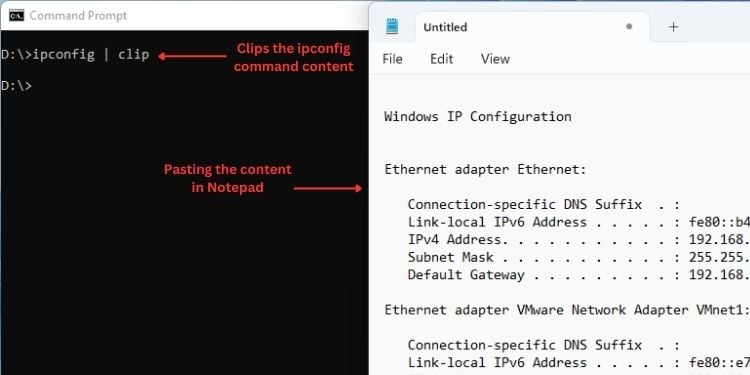

คำสั่งนี้ คัดลอกเอาต์พุตที่ดำเนินการจากคำสั่งบางคำสั่งไปยังคลิปบอร์ดของ Windows ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณสามารถคัดลอกข้อมูลไปยังโปรแกรมอื่นได้โดยตรง
การคัดลอกไฟล์ข้อความหรือสคริปต์โดยตรงมีประโยชน์อย่างมากโดยไม่ต้องเปิด ต่อไปนี้คือพารามิเตอร์ที่เกี่ยวข้อง:
เวอร์ชัน
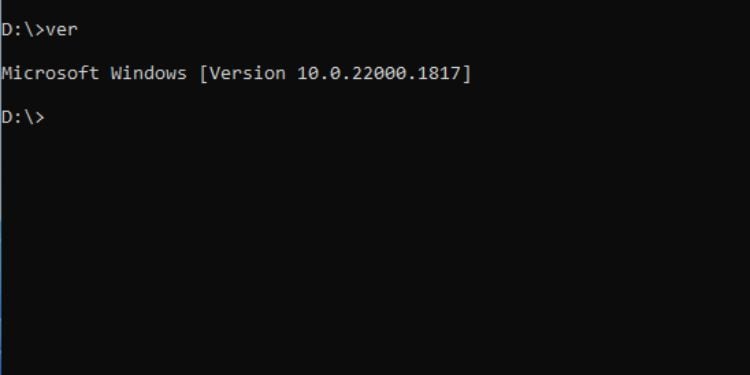

Command Prompt ช่วยให้ ดูหมายเลขเวอร์ชันของ Windows ได้อย่างรวดเร็วที่สุดโดยใช้คำสั่งง่ายๆ ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณสามารถระบุได้ว่ามีการติดตั้ง Windows เวอร์ชันล่าสุดบนคอมพิวเตอร์ของคุณหรือไม่
ไวยากรณ์: ver
คำสั่งของระบบ
ไม่ว่าคุณกำลังพยายามเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับคอมพิวเตอร์ของคุณหรือทำงานบางอย่างเกี่ยวกับระบบ คำสั่งต่อไปนี้อาจมีประโยชน์:
Powercfg
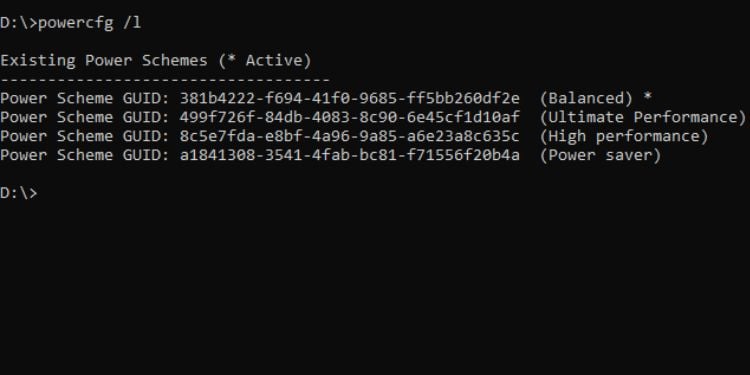

ยูทิลิตี้พร้อมรับคำสั่งนี้ช่วยให้คุณสามารถ ควบคุมการตั้งค่าพลังงานโดยรวม ของคอมพิวเตอร์ของคุณ โปรดทราบว่าหากคุณใช้พารามิเตอร์นี้โดยไม่มีพารามิเตอร์ที่เหมาะสม คุณจะพบข้อผิดพลาด”พารามิเตอร์ไม่ถูกต้อง”
แม้ว่าจะมีพารามิเตอร์มากมาย แต่เราจะพูดถึงเฉพาะพารามิเตอร์ที่พบบ่อยที่สุดด้านล่างเท่านั้น หากต้องการเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม เพียงเรียกใช้ powercfg/?
หากต้องการเรียนรู้คำสั่งด้านบน โดยละเอียด ผมแนะนำให้รัน powercfg/? คำสั่ง <พารามิเตอร์>
ตัวอย่างเช่น หากคุณต้องการทราบข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับพารามิเตอร์/list คุณสามารถเรียกใช้ powercfg/list ได้
Shutdown
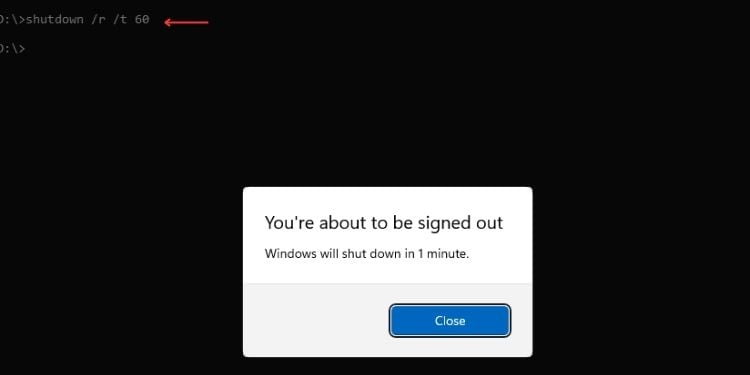

น่าสนใจ คุณสามารถ ปิดคอมพิวเตอร์ของคุณ โดยใช้คำสั่งเดียวบน Command Prompt นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถกำหนดเวลากระบวนการปิดเครื่องได้ตามที่คุณต้องการ
ต่อไปนี้เป็นพารามิเตอร์ทั่วไปที่อาจมีประโยชน์:
หมายเหตุ: การดำเนินการปิดระบบโดยไม่มีพารามิเตอร์จะเรียกใช้ help หรือ/? สำหรับคำสั่งปิดเครื่อง
Driverquery
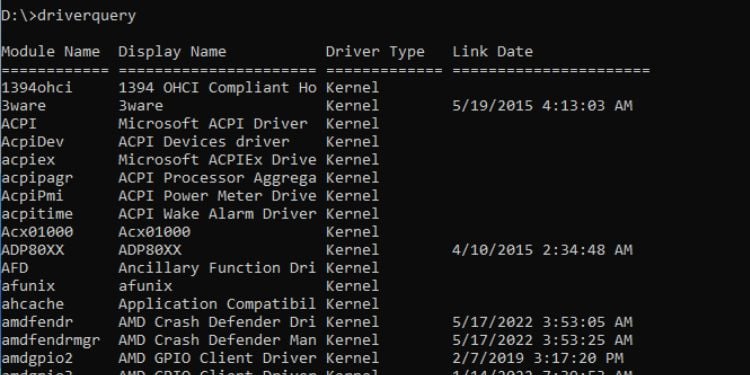

ต่อไป ไดรเวอร์อุปกรณ์ เป็นส่วนประกอบที่สำคัญของคอมพิวเตอร์ หากคุณต้องการข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับพวกเขา เรามียูทิลิตี้ตัวจัดการอุปกรณ์บน Windows GUI แล้ว
อย่างไรก็ตาม หากคุณต้องการแสดงข้อมูลไดรเวอร์โดยละเอียดในขณะที่ทำงานบนอินเทอร์เฟซบรรทัดคำสั่ง คุณเพียงแค่พิมพ์คำค้นหาไดรเวอร์และ กด Enter
นอกจากนั้น คุณสามารถใช้พารามิเตอร์ต่อไปนี้ซึ่งแต่ละตัวมีฟังก์ชันแยกกัน:
ชื่อโฮสต์

คำสั่งนี้ พิมพ์ชื่ออุปกรณ์ หากคุณไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับของคุณหรือกำลังพยายามระบุชื่อโฮสต์บนคอมพิวเตอร์เครื่องอื่น เพียงพิมพ์ชื่อโฮสต์และกด Enter ใน Command Prompt ก็จะแสดงผล
ไวยากรณ์: ชื่อโฮสต์
ข้อมูลระบบ
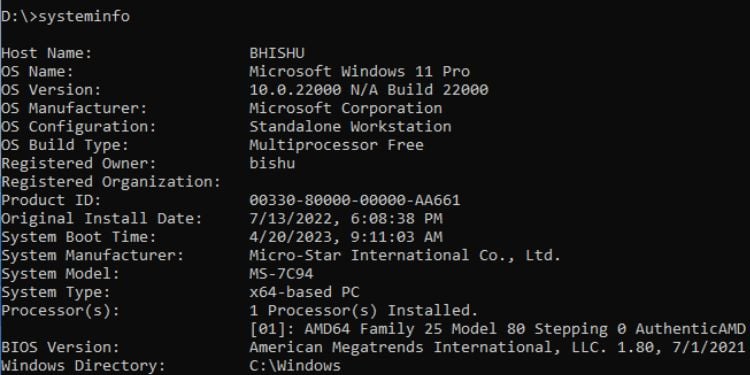
ไม่เหมือนกับคำสั่งชื่อโฮสต์ ซึ่งจะพิมพ์ข้อมูลโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับคอมพิวเตอร์ของคุณ โดยพื้นฐานแล้ว ก็เหมือนกับการเปิดแอปพลิเคชันข้อมูลระบบเพื่อตรวจสอบข้อมูลจำเพาะของพีซีของคุณ
นอกจากนี้ คุณสามารถใช้พารามิเตอร์เดียวกับที่ใช้ใน devicequery (/s,/u,/p,/fo,/nh,/si และ/v) เพื่อพิมพ์ผลลัพธ์ในรูปแบบที่คุณต้องการ
ไวยากรณ์: systeminfo [พารามิเตอร์]
คำสั่งแก้ไขปัญหา Windows
หากคุณประสบปัญหาเกี่ยวกับ Windows อาจ เกิดจากหลายสาเหตุ เช่น ไดรฟ์เสียหาย ไฟล์ระบบ รูปภาพ หรืออื่นๆ อีกมากมาย โดยปกติแล้ว การเรียกใช้เครื่องมือแก้ปัญหาและคำสั่งที่เป็นประโยชน์สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้ และนั่นคือสิ่งที่ฉันจะกล่าวถึงในส่วนนี้
CHKDSK

คำสั่งนี้จะตรวจสอบดิสก์ภายในเครื่องในคอมพิวเตอร์และแจ้งผู้ใช้เกี่ยวกับข้อผิดพลาดทางตรรกะและทางกายภาพ โปรดทราบว่าการแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดจะทำได้ก็ต่อเมื่อคุณใช้พารามิเตอร์ต่อไปนี้อย่างชาญฉลาด
ในที่นี้ ข้าพเจ้าได้กล่าวถึงเฉพาะเรื่องทั่วไปเท่านั้น แต่ถ้าคุณต้องการเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม นี่คือคำแนะนำฉบับสมบูรณ์เกี่ยวกับวิธีเรียกใช้ CHKDSK เพื่อซ่อมแซมและแก้ไขฮาร์ดไดรฟ์
SFC

Windows System File Checker (SFC) ช่วยคุณ ซ่อมแซมไฟล์ Windows ที่เสียหาย มันทำงานโดยแทนที่ไฟล์ที่เสียหายด้วยสำเนาแคช ซึ่งสามารถเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของคอมพิวเตอร์ได้
ต่อไปนี้เป็นคำสั่ง SFC บางส่วนที่ใช้มากที่สุด:
DISM

คำสั่งนี้เริ่มเครื่องมือ Deployment Image Service and Management เพื่อกำหนดค่า คุณลักษณะและแพ็คเกจของอิมเมจ Windows มีคำสั่ง DISM มากมายเพื่อใช้เมื่อแก้ไขปัญหา Windows รวมถึง FFU, WIM, Imaging และอื่นๆ แต่ฉันจะพูดถึงพารามิเตอร์ทั่วไปเท่านั้น
เพื่อความสะดวกของคุณ เราได้จัดทำคำแนะนำโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับการเรียกใช้คำสั่ง DISM ต่างๆ แล้ว
เคล็ดลับเพิ่มเติม: ถึง เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับแต่ละคำสั่ง คุณสามารถดำเนินการ/? พารามิเตอร์ในตอนท้าย ตัวอย่างเช่น หากคุณต้องการทราบข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ/image เพียงดำเนินการ dism.exe/image/?
msdt.exe-id DeviceDiagnostic
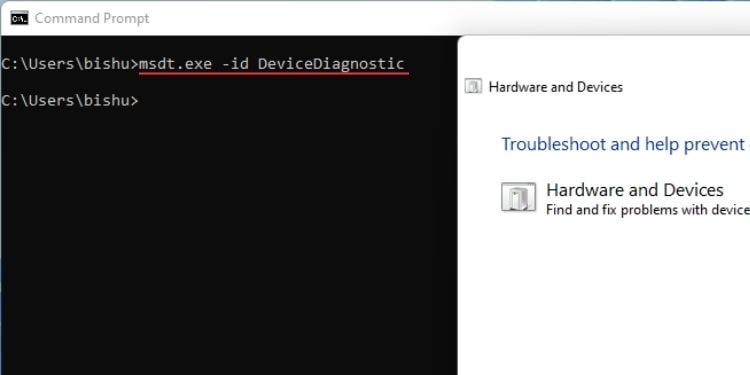

เครื่องมือแก้ปัญหาฮาร์ดแวร์และอุปกรณ์ ไม่สามารถใช้กับเครื่องมือแก้ปัญหาอื่นๆ ในการตั้งค่า Windows ได้อีกต่อไป อย่างไรก็ตาม ยูทิลิตีสามารถค้นหาและแก้ไขปัญหาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับส่วนประกอบฮาร์ดแวร์ทั้งหมดได้
ใน Windows 11 คุณสามารถเปิดใช้งานได้โดยใช้คำสั่ง msdt.exe-id DeviceDiagnostic บน Command Prompt
คำสั่งการจัดการไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรี
การจัดการไฟล์และ ไดเร็กทอรีบน Command Prompt อาจยุ่งยากเล็กน้อย อย่างไรก็ตาม ต่อไปนี้คือคำสั่งพื้นฐานบางส่วนที่สามารถทำให้งานของคุณง่ายขึ้น
DIR
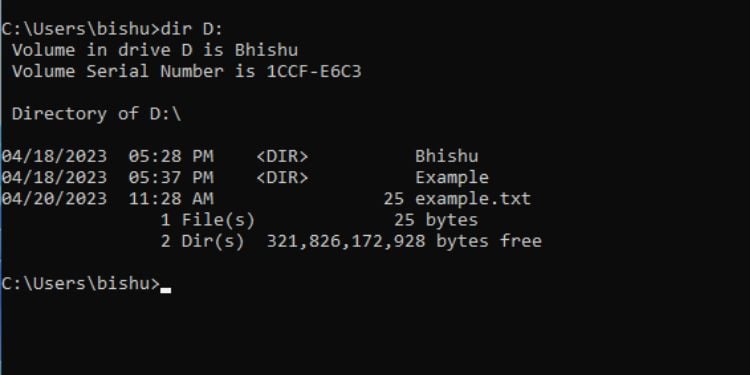

สิ่งนี้ คำสั่ง แสดงไฟล์และไดเรกทอรี/ไดเรกทอรีย่อยทั้งหมด จากไดรฟ์/ไดเรกทอรีที่ระบุ
ผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่ใช้คำสั่งนี้เพื่อแสดงรายการไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรี สามารถทำได้โดยใช้คำสั่ง dir นอกจากรายการแล้ว ยังแสดงฉลากของวอลุ่ม หมายเลขซีเรียล และจำนวนไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรีทั้งหมด
นอกเหนือจากนั้น คุณยังสามารถใช้พารามิเตอร์ต่อไปนี้:
Copy
ตามชื่อที่แนะนำ คำสั่งนี้ คัดลอกไฟล์จากที่หนึ่งไปยังอีกที่หนึ่ง โปรดทราบว่าจะสร้างสำเนาแทนการย้าย
ไวยากรณ์: คัดลอก [ชื่อไฟล์] [เส้นทาง]
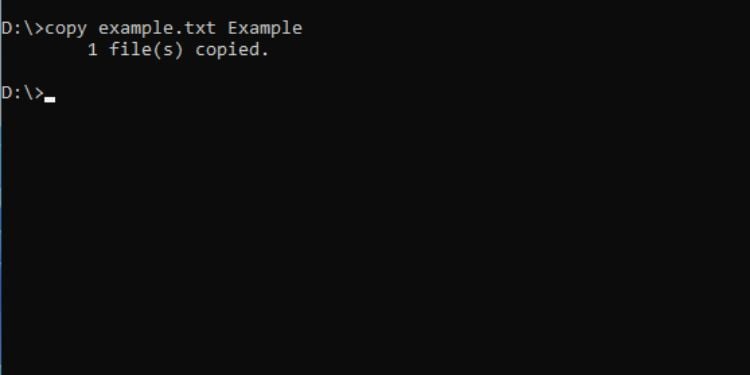

ตัวอย่างเช่น หากต้องการคัดลอกไฟล์ example.txt จากไดรฟ์ D ไปยังโฟลเดอร์ Example ในไดรฟ์เดียวกัน นี่คือคำสั่ง I’จะใช้:
copy example.txt Example
Move
คำสั่งนี้ทำงานในลักษณะเดียวกับการคัดลอก อย่างไรก็ตาม ความแตกต่างก็คือ ย้ายไฟล์จากที่หนึ่งไปยังอีกที่หนึ่ง โดยพื้นฐานแล้วเป็นเทคนิคการตัดและวางที่เราใช้ใน GUI ของ Windows
ไวยากรณ์: ย้าย [ชื่อไฟล์] [เส้นทาง]
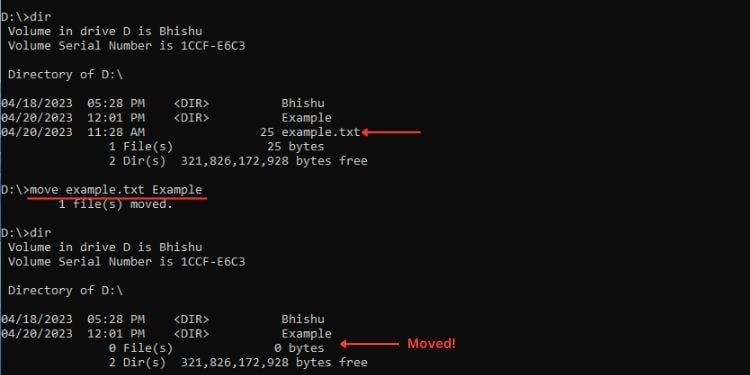

ตัวอย่างเช่น หากต้องการย้ายไฟล์ example.txt จากไดรฟ์ D ไปยังโฟลเดอร์ Example ในไดรฟ์เดียวกัน นี่คือ คำสั่งที่ฉันจะใช้:
move example.txt Example
Del or Erase
ทั้งคำสั่ง Del และ Erase สามารถใช้เพื่อ ลบอย่างถาวร ไฟล์ ซึ่งหมายความว่าคุณไม่สามารถเรียกไฟล์กลับจากถังรีไซเคิลได้
ไวยากรณ์: del [ชื่อไฟล์]
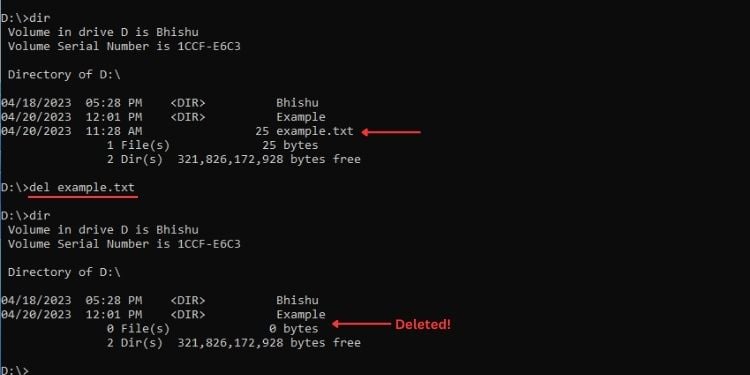

ตัวอย่างเช่น หากต้องการลบไฟล์ example.txt อย่างถาวร ฉันจะใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
del example.txt
หมายเหตุ: แม้ว่าเราจะไม่ได้ระบุพารามิเตอร์และแอตทริบิวต์สำหรับการคัดลอก ย้าย และ del แต่คุณก็ทดสอบด้วยตัวคุณเองได้โดยใช้วิธีใช้หรือ/? พารามิเตอร์.
MKDIR หรือ MD
ทั้งคำสั่ง MKDIR และ MD ใช้เพื่อ สร้างไดเร็กทอรี (โฟลเดอร์) ใหม่ คุณสามารถทำได้ในไดเร็กทอรีปัจจุบันหรือแม้แต่ในไดเร็กทอรีอื่นโดยตรง หมายความว่าคุณไม่จำเป็นต้องย้ายไปยังไดรฟ์/ไดเร็กทอรีนั้นเพื่อสร้างไดเร็กทอรี
Syntax: mkdir [path ]\[ชื่อไดเรกทอรี]
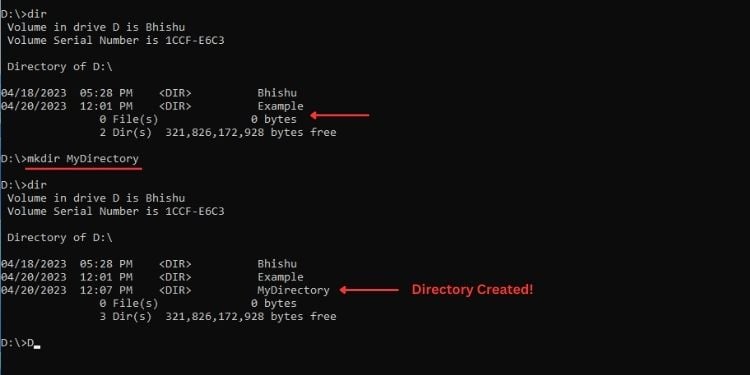

ตัวอย่างเช่น ถ้าฉันอยู่ใน D drive และต้องการสร้างไดเรกทอรีใหม่ นี่คือคำสั่งที่ฉันจะใช้:
mkdir MyDirectory
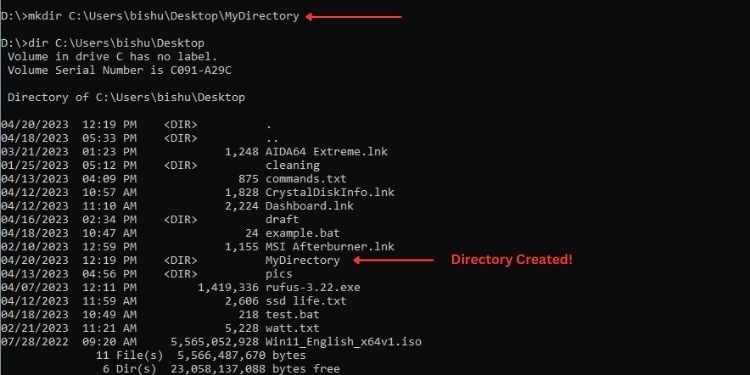
แต่หากต้องการสร้างไดเร็กทอรีใหม่ในเส้นทางเฉพาะ ฉันจะดำเนินการดังนี้:
mkdir C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDirectory
Rename หรือ Ren
คำสั่ง Ren หรือ Rename เพียงแค่ กำหนดค่าชื่อไฟล์หรือไดเรกทอรีใหม่ ขณะดำเนินการ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าคุณไม่ได้ทำซ้ำชื่อกับไฟล์/ไดเร็กทอรีอื่น
ไวยากรณ์: ren [path]/[filename] [new_filename]
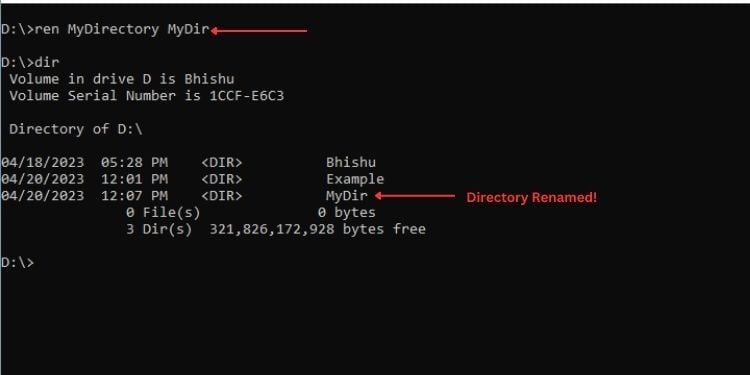
จากตัวอย่างเดียวกับด้านบน นี่คือวิธีที่ฉันจะเปลี่ยนชื่อไฟล์สองไฟล์ที่ฉันสร้างไว้ก่อนหน้านี้:
ren MyDirectory MyDir
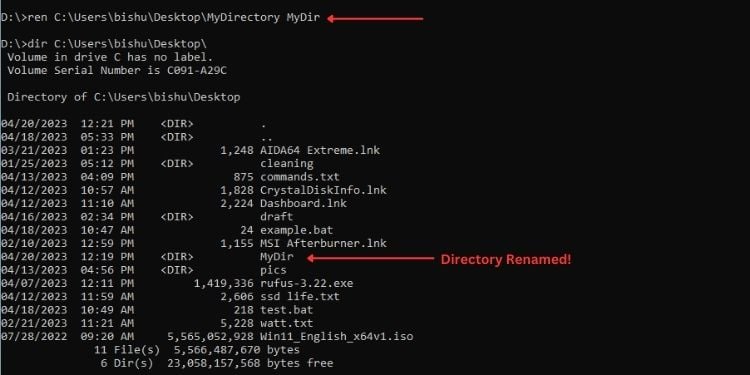
ren C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDirectory MyDir

RMDIR หรือ RD
ย่อมาจาก ‘ลบไดเรกทอรี’ และนั่นคือสิ่งที่คำสั่งทำ คุณยังสามารถใช้คำสั่งที่สั้นกว่าซึ่งดำเนินการแบบเดียวกัน – RD
ต่อไปนี้คือพารามิเตอร์ทั้งหมดสำหรับคำสั่ง RMDIR:
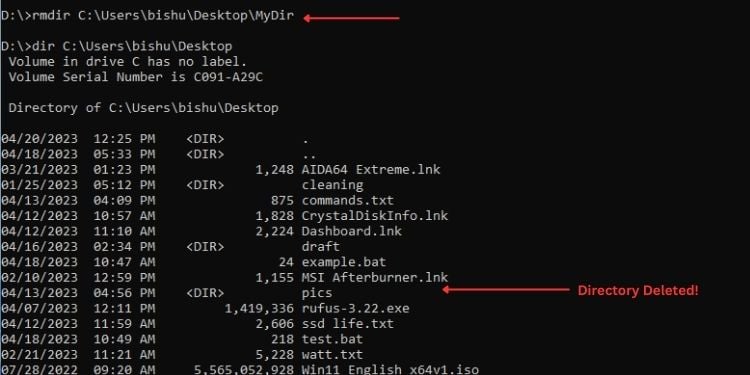
ตามตัวอย่าง ผมจะแสดงวิธีลบไฟล์ MyDirectory ที่ ฉันสร้างไว้ก่อนหน้านี้:
rmdir MyDir
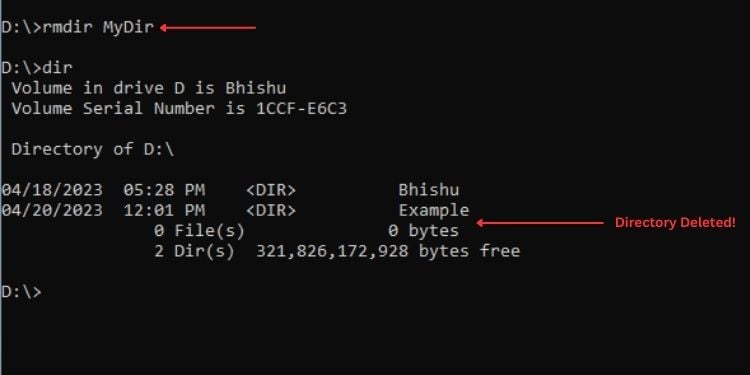

rmdir C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDir

ประเภท
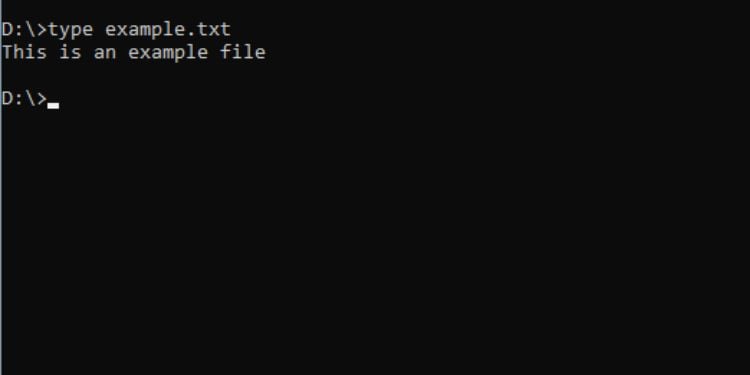

คำสั่งนี้ใช้เพื่อ แสดงเนื้อหาของไฟล์ข้อความบน Command Prompt ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณไม่ต้องไปยังตำแหน่งที่ต้องการ เปิดไฟล์และปิดอีกครั้งหากไม่จำเป็น
ไวยากรณ์: พิมพ์ [เส้นทาง] [ชื่อไฟล์]
คุณสามารถข้าม [เส้นทาง] หากคุณอยู่ในไดเร็กทอรีเดียวกับไฟล์ข้อความ
รอง


คำสั่งนี้ใช้เพื่อ แสดงหรือจัดการความสัมพันธ์ของนามสกุลไฟล์ต่างๆ โปรดทราบว่าคุณต้องการสิทธิ์ของผู้ดูแลระบบในการแก้ไขการเชื่อมโยง
หากคุณเพียงเรียกใช้คำสั่ง assoc ยูทิลิตีบรรทัดคำสั่งจะแสดงส่วนขยายทั้งหมดพร้อมกับประเภทไฟล์ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ไวยากรณ์: assoc
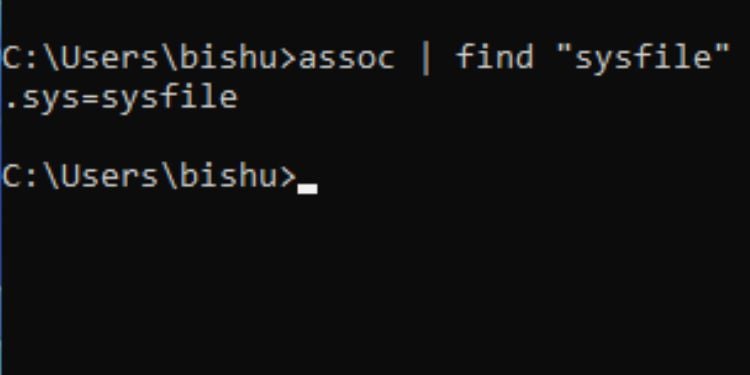
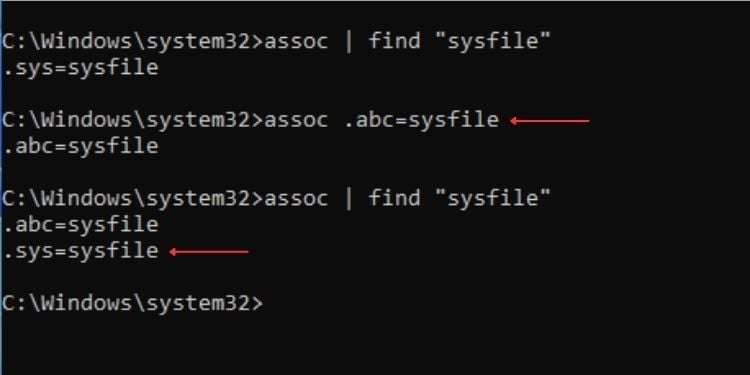
นอกจากนี้ คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่านามสกุลไฟล์ใดเชื่อมโยงกับไฟล์แต่ละประเภท ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสามารถค้นหาส่วนขยายทั้งหมดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ’sysfile’ตามที่แสดงในตัวอย่างด้านล่าง
ไวยากรณ์: assoc | ค้นหา “[ประเภทไฟล์]”
ตัวอย่าง:assoc | ค้นหา “sysfile”

คุณสามารถแก้ไขการเชื่อมโยงได้เช่นกัน คุณสามารถเชื่อมโยงนามสกุลไฟล์กับไฟล์ประเภทใดก็ได้ที่คุณต้องการ
ไวยากรณ์: assoc=
ตัวอย่าง: assoc.abc=sysfile

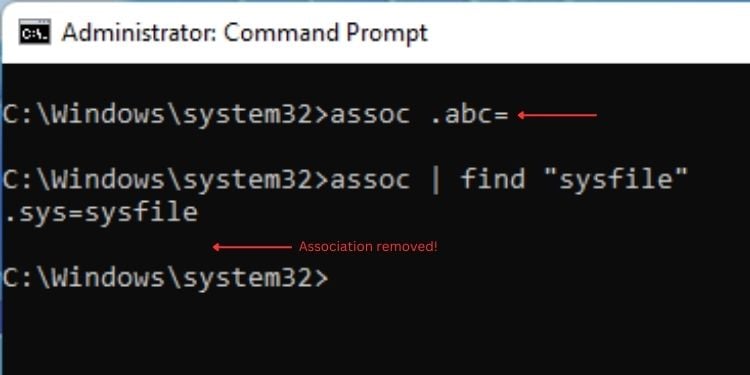
สุดท้าย คุณสามารถลบ สมาคม. อย่างไรก็ตาม คุณจะต้องรีสตาร์ทคอมพิวเตอร์เพื่อใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลง
ไวยากรณ์: assoc [ส่วนขยาย]=
ตัวอย่าง: assoc.abc=

FC
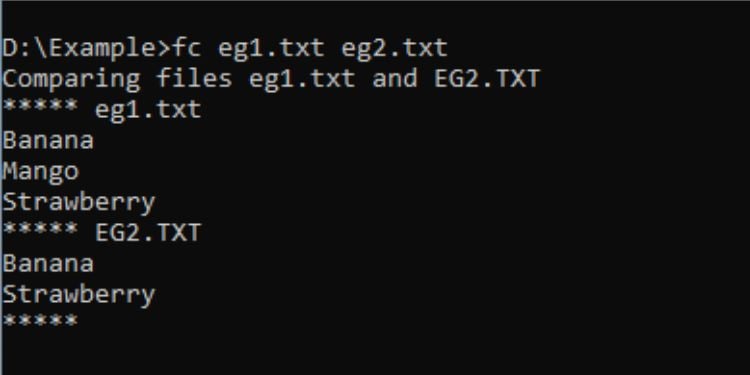

FC ย่อมาจาก”การเปรียบเทียบไฟล์”ซึ่งฟังดูแล้ว ใช้สำหรับ เปรียบเทียบไฟล์สองไฟล์ เพื่อให้คุณสามารถเรียนรู้ เกี่ยวกับความแตกต่าง ดังที่แสดงในการสาธิตด้านบน ฉันได้เปรียบเทียบไฟล์ข้อความสองไฟล์เพื่อทราบความแตกต่างของรายการภายในไฟล์เหล่านั้น
ไวยากรณ์: fc [file1] [file2]
ต่อไปนี้เป็นพารามิเตอร์ที่มีประโยชน์สำหรับคำสั่ง FC:
Attrib
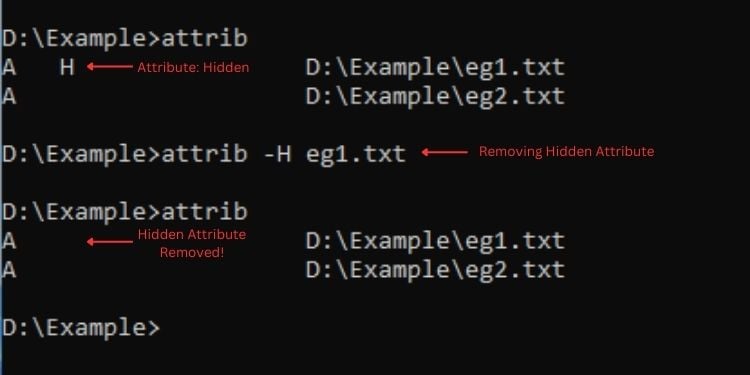
คำสั่งนี้ จัดการแอตทริบิวต์สำหรับไฟล์และโฟลเดอร์ คุณสามารถตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์อะไรก็ได้ที่คุณต้องการ เช่น ซ่อน อ่านอย่างเดียว ระบบ และอื่นๆ หากต้องการตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ ให้ใช้’+’และหากต้องการลบ ให้ใช้’-‘
ไวยากรณ์: attrib [+/-][attribute_value] [ชื่อไฟล์/โฟลเดอร์]
หมายเหตุ: ฉันยังไม่ได้ กล่าวถึงพารามิเตอร์สำหรับแอตทริบิวต์ (/s,/d และ/l) คุณสามารถใช้/? เปลี่ยนเพื่อเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับพวกเขา
ต้นไม้
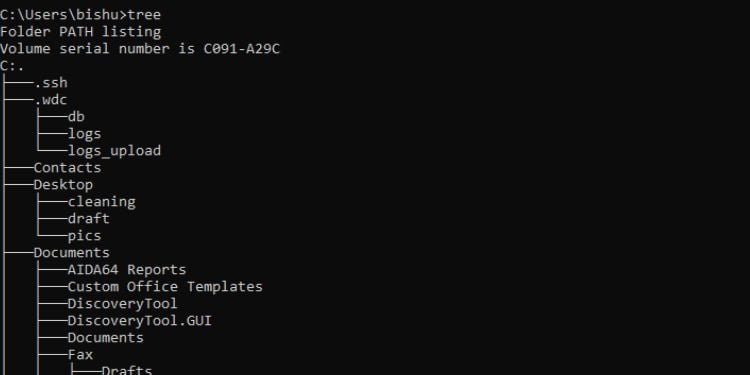

หากคุณต้องการ หากต้องการดูไดเรกทอรีย่อยภายในไดเรกทอรีหรือไดรฟ์ คำสั่ง tree จะทำให้ ดูสวยงามทางกราฟิก จัดโครงสร้างเอกสารในรูปแบบที่ดูง่าย สิ่งที่คุณต้องทำคือรันคำสั่ง tree และระบุพาธหากจำเป็น
ไวยากรณ์: tree [path]
ด้านล่างนี้คือพารามิเตอร์สองตัวที่คุณสามารถนำมาใช้กับคำสั่ง tree:
คำสั่งการจัดการดิสก์/ไดรฟ์
นอกเหนือจากการจัดการไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรีแล้ว คุณยังสามารถกำหนดค่าดิสก์และไดรฟ์ใน Command Prompt
ต่อไปนี้คือ 7 คำสั่งที่ใช้มากที่สุดสำหรับจุดประสงค์นี้:
Vol
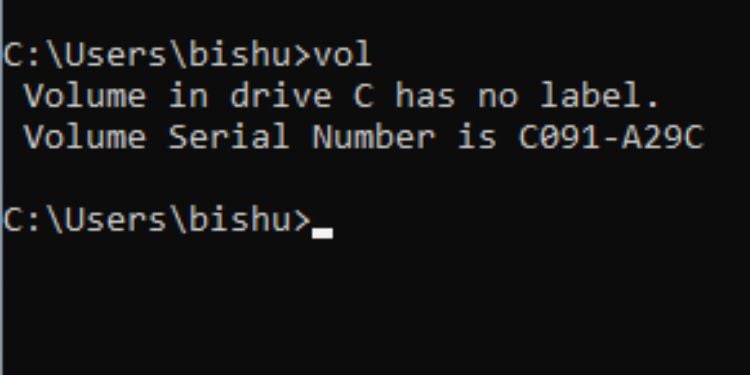

นี่คือคำสั่งเพื่อตรวจสอบชื่อวอลุ่มหรือหมายเลขประจำเครื่องอย่างรวดเร็ว สิ่งที่คุณต้องทำคือเรียกใช้ vol ด้วยอักษรชื่อไดรฟ์
ไวยากรณ์: vol [dirve_letter]:
รูปแบบ
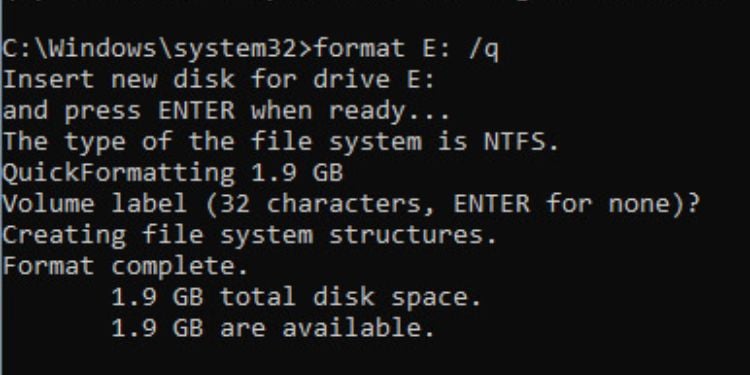

While there already exists easy-to-use GUI applications for formatting your disk drives, it’s never a bad idea to learn this on Command Prompt.
If you want to format a hard drive having just one partition, the format command should work out for you. However, the better option would be using diskpart, which I shall discuss below.
Here, I’ll only mention the common parameters. Nonetheless, you can go through the other guide that should help you format a hard drive from CMD in detail.
Diskpart
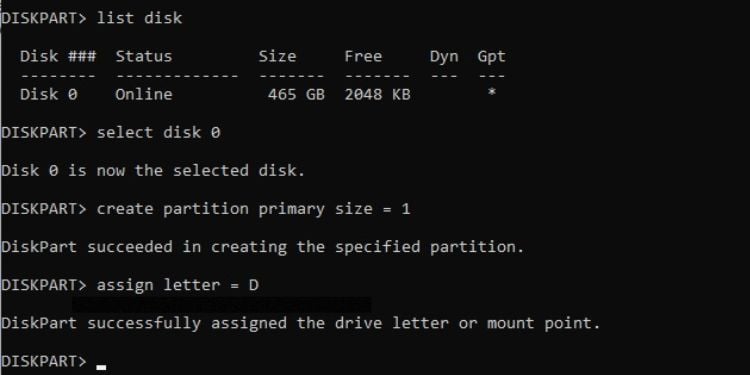

This is a command-line interpreter that offers disk management features on Command Prompt. With this utility, you can assign drive letters, manage the drive attributes, configure partitions, display disk information, format a drive, and much more.
Type diskpart and this should launch the interpreter. However, you require administrative privilege to use it.
In the table below, I have mentioned the most used commands in Diskpart. If you wish to learn more about disk partitions using the diskpart command, you can check out our dedicated guides for both HDD and SSD.
Defrag
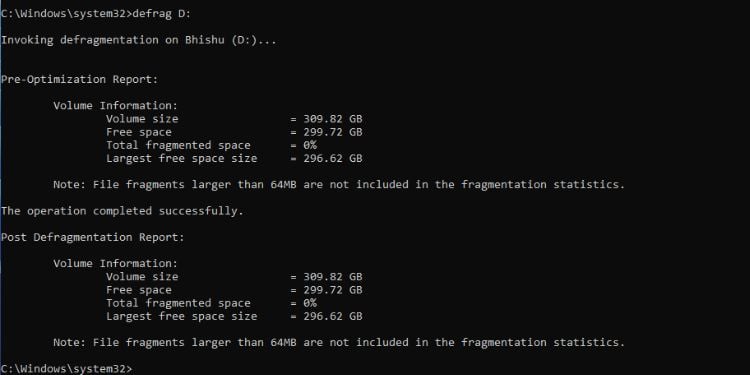

Defragmentation simply means reorganizing the data inside an HDD to achieve better performance (not recommended on SSD).
Like any other action, Windows already offers a dedicated utility.
However, if you wish to know this in detail, Command Prompt offers tons of parameters that should help you out. Note that this command requires administrative privilege.
Diskusage
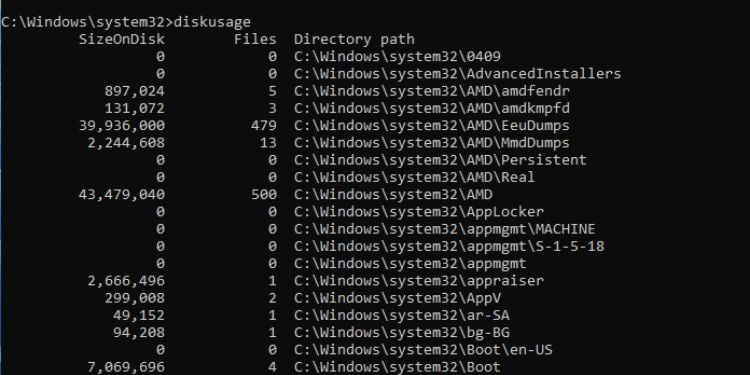

This might not be the most used command but is definitely worth it. You can get the summarized details on the selected disk’s usage in no time.
Simply executing the diskusage command should do the job (note that you need to open CMD as an administrator). Along with that, you can take a look at the following parameters that might be beneficial:
Networking Commands
Unlike others, networking commands are widely used mainly for troubleshooting purposes. In fact, fetching IP addresses or configuring network settings is much easier on Command Prompt than using GUI components.
If you’re a networking enthusiast, here are the commands that you need to focus on:
Net
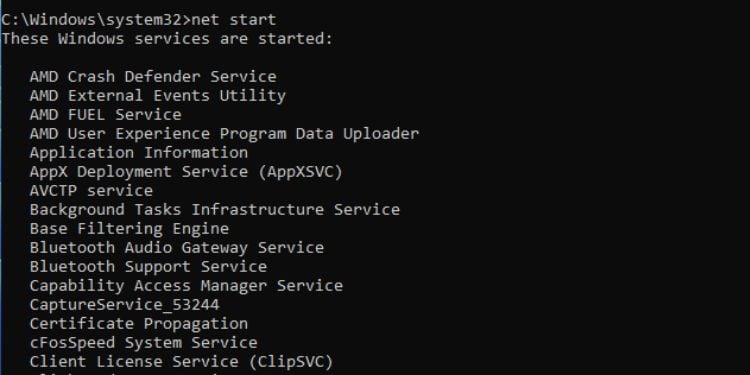

You can use this command to manage different networking services. It comes with multiple options each performing a specialized task.
Here, I’ve only mentioned the most common ones. You can execute the net command without a parameter to get more.
Ipconfig
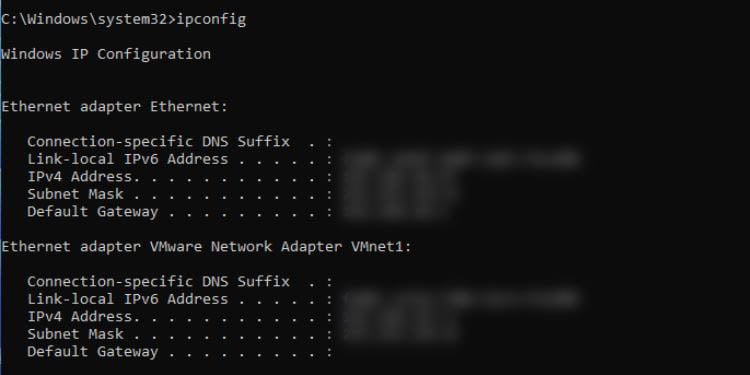

This command is for network configuration and management. You can view the detailed Windows TCP/IP information, release/renew IP addresses, flush the DNS cache, and much more.
Executing ipconfig without parameters displays the IPv4, IPv6, subnet mask, and default gateway for every adapter. For other purposes, you can adopt the following parameters:
Netsh
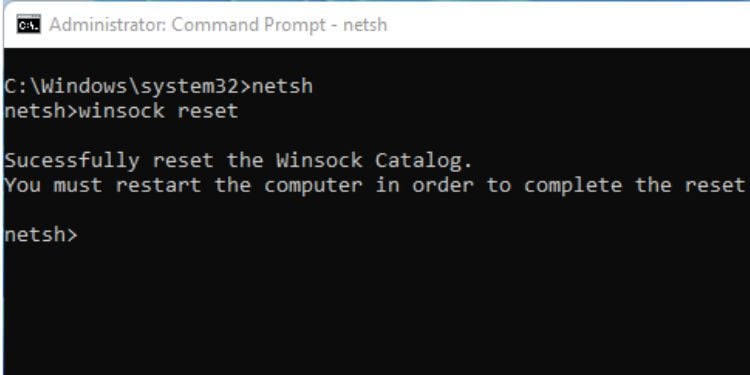

This is another essential networking command used for managing network configurations. You can execute netsh to launch the dedicated shell. After that, you can perform desired networking operations using some of the well-known parameters from the below table:
Additional Tip: You can further learn about each of the above command’s arguments using ? in the netsh shell or use the/? parameter with the netsh command.
Netstat
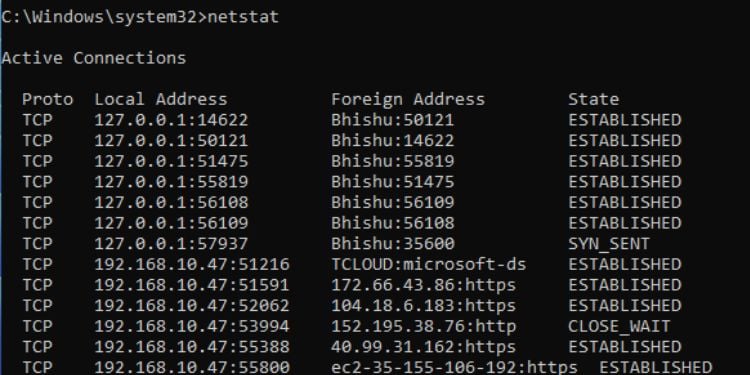

This command lists the active connections on your computer. It displays the protocol, local as well as foreign address, and the current state. Just executing the netstat command will list the active TCP connections.
To display other protocols, here are some parameters you can use:
Ping
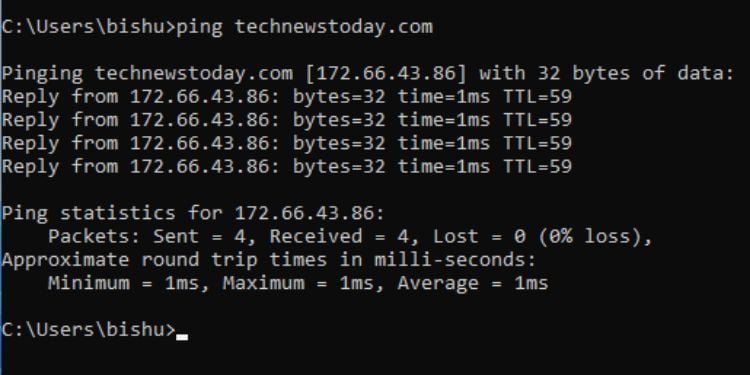

This command is widely used for testing host-server reachability and internet connectivity. Executing ping displays the IP address statistics and the approximate round trips in milliseconds.
Here are a few parameters that I recommend trying out:
Tracert
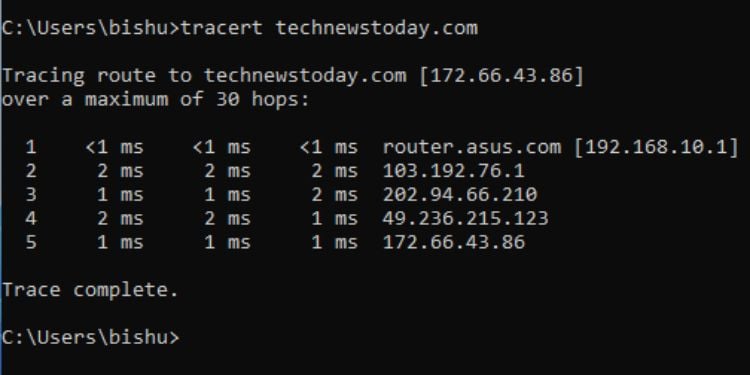

This command traces the route to a certain IP or domain by sending ICMP or ICMPv6 messages with increasing TTL values. It’s extremely useful during network troubleshooting as it informs users about the routing issues and validates the network paths.
Implementing the tracert command without a parameter traces the route of the specified domain/IP over a maximum of 30 hops.
Nevertheless, you could make use of the following parameters to gain additional networking information:
Pathping
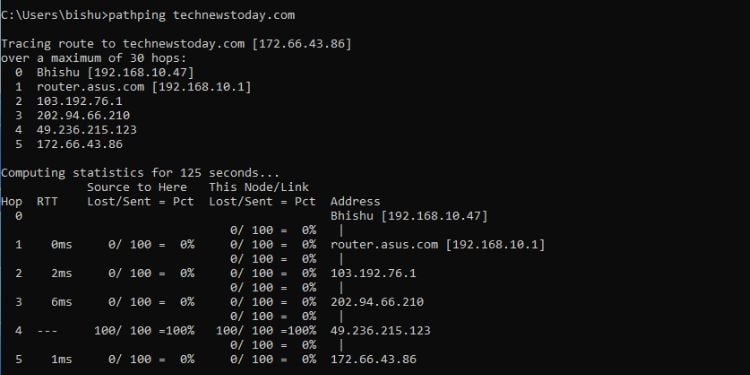

This command is a combination of Tracert and Ping. When executed without a parameter, it traces the route to the target over a maximum of 30 hops and computes statistics for 125 seconds (by default).
Here are some of the most used pathping parameters:
Getmac
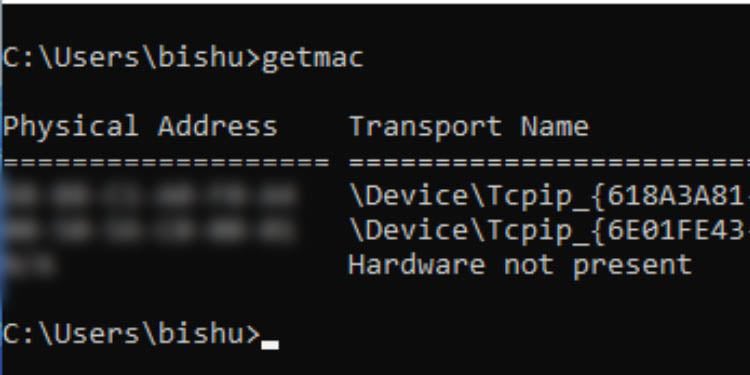

If you wish to get the MAC address of your computer, you can execute the getmac command and this will display the result in no time. The result includes both the physical address and the transport name.
Along with that, I highly recommend trying out the following parameters:
NSLookUp
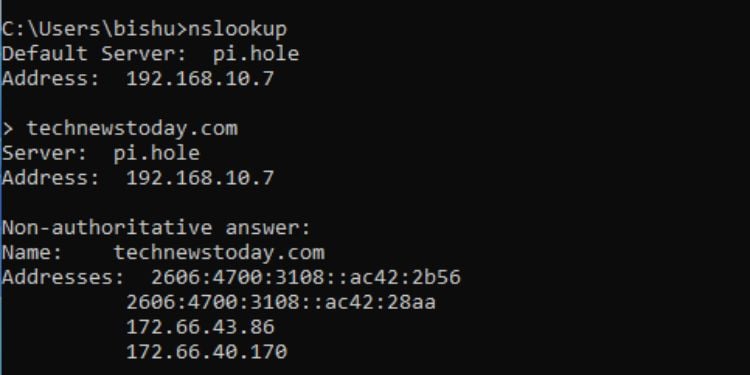

This is yet another command-line utility that includes numerous commands to obtain domain name or IP address information. To start the prompt, simply type nslookup in the Command Prompt and hit Enter.
While there are countless parameters for nslookup, I’m only going to focus on a few common ones in the table below:
Miscellaneous
If you have implemented each of the commands I’ve discussed, you should now be proficient enough to use Command Prompt. However, the aforementioned commands are not enough to master this Windows command-line interface.
There are thousands more, and it’s impossible for me to include all of them in this single post.
For now, I would recommend trying out the following commands that could come in handy while you’re on the way to mastering Command Prompt:
Tasklist
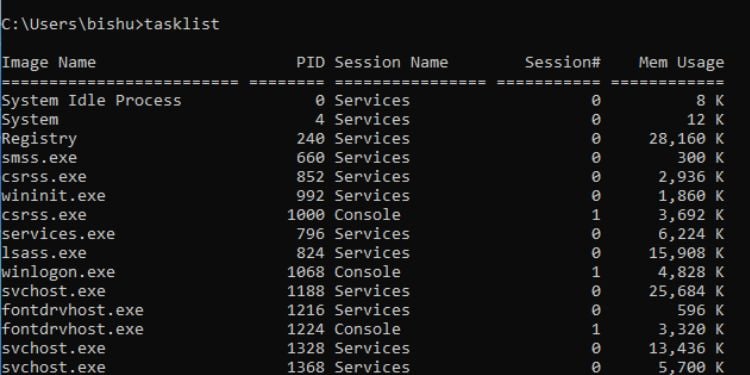

You can use this command to display the currently running processes on your computer. Executing tasklist lists down the name of the process, its PID, session name, session number, and memory usage. Also, you can try out the following parameters:
Taskkill
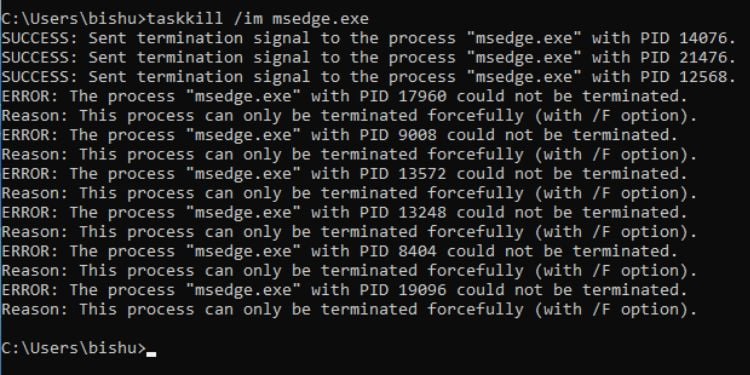

While the tasklist command displays the processes, taskkill kills/ends them. You can use either process ID or image name to do this task. Therefore, you need to utilize any of the following common parameters:
Powershell
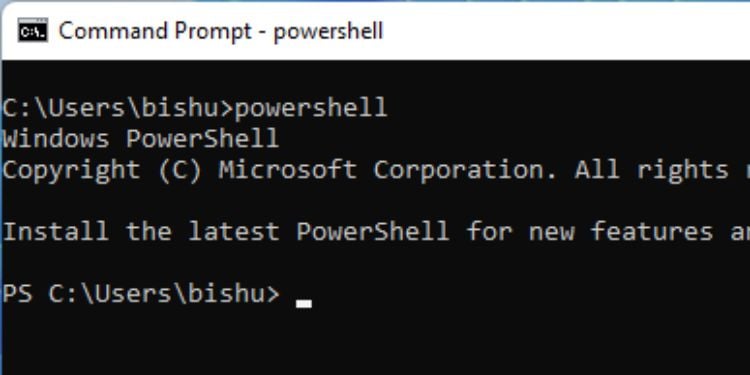

If you prefer Windows PowerShell over CMD, you can actually run the Command Prompt as a Powershell window. Just type powershell and hit Enter. You’ll likely get the PS prefix indicating that you can now run all the Powershell cmdlets here.
Syntax: powershell
Set
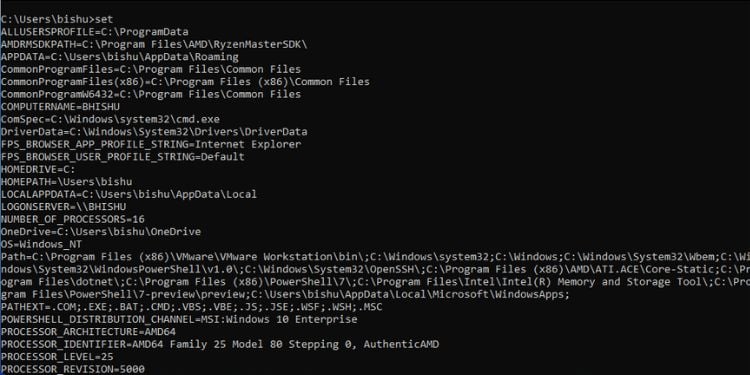

This command is used for configuring the Windows environment variables. To display all the available ones, you can use the set command without any parameters. In order to set a new environment variable, you can use a variable name and provide the necessary value.
Syntax: set [variable_name]=[value]
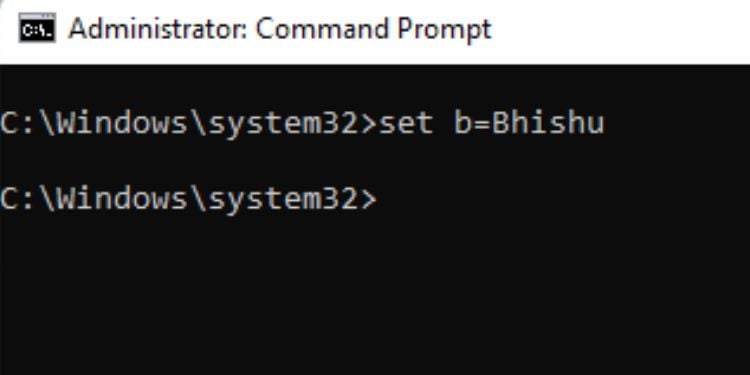

Likewise, it’s possible to delete any environment variable too. Below is the syntax that should clear your doubt.
Syntax: set [variable_name]=
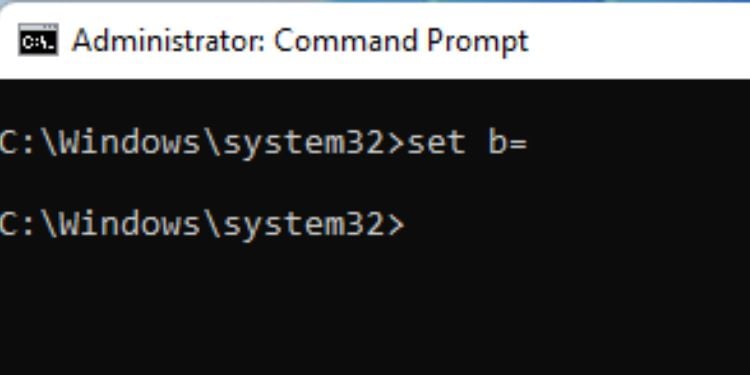

The set command on Command Prompt has the following two parameters with individual functionality:
Start
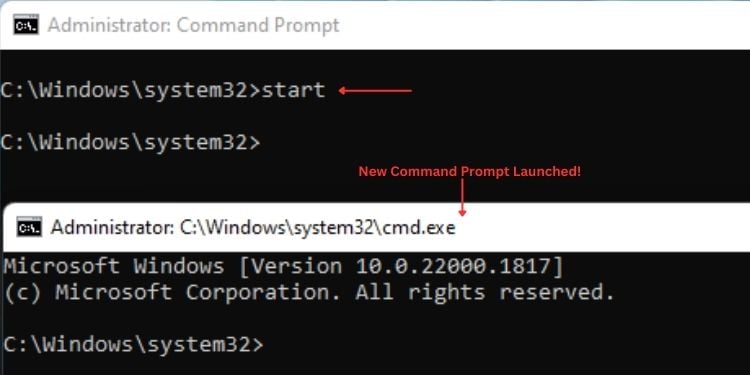

You can use this command to launch a new Command Prompt window. Without the use of any parameter, it will simply launch the new prompt. However, utilizing the following parameters can help you perform just more than that:
BCDBoot
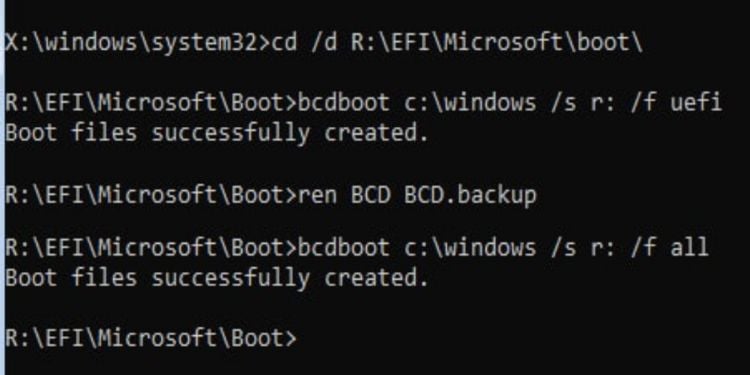

Most users utilize this command to repair the boot environment from the Windows Recovery Environment. It works by copying the Windows installation files to a system partition. You need to execute bcdboot with the following parameters:
Date
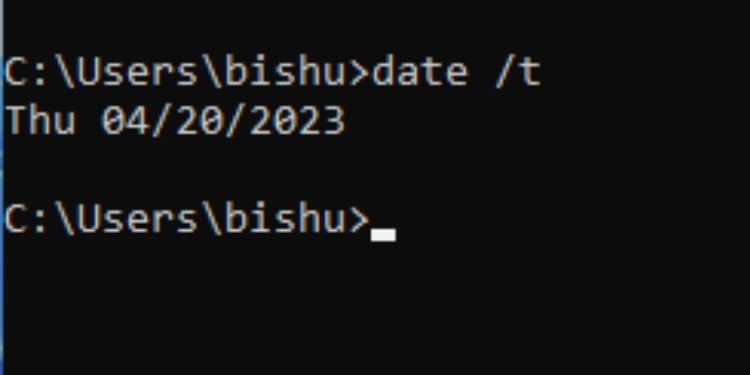

This is another useful command to quickly check the current date. You can display or set a new date as per your requirement. If you execute just the date command, the prompt displays the date and asks you to set a new one. But if you quickly want to check the date, use the/t parameter.
Syntax: date/t
Prompt
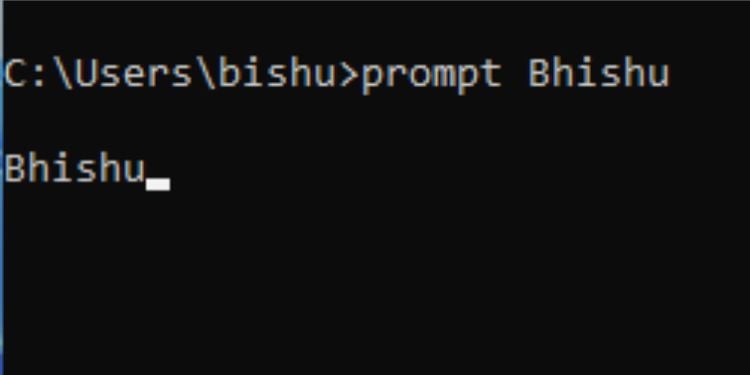

This command offers customization of the text that appears in front of the cursor (by default, it’s the current directory path).
You can change this to any character string of your choice or predefined characters (like current date, drive, path, times, windows version, etc.) using special codes. You can check using the/? Parameter. To switch back to the normal format, execute the prompt without any parameters.
Syntax: prompt [text/special_code]
Color
Certainly, you have thought of customizing the Command Prompt. To your surprise, it’s possible to tweak the default black (background) and white (foreground/text) combination. For this, you require specifying two hex digits—the first representing the background and the second corresponding to the text.
Syntax: color [hexcode]
As per the above table, let’s say you want a red background with light blue text. So, you’ll have to execute the following command:
color 49
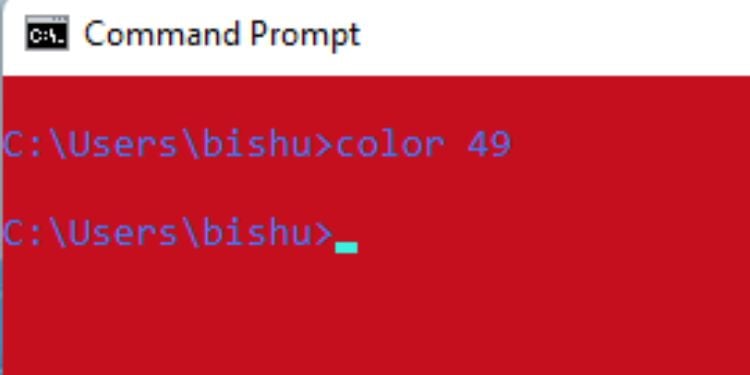

While you’re at it, note that you cannot set the same background and foreground colors. Even if you do it, the command will not execute and you’ll be left with the existing combination.
To switch back to default, run the color command without any parameter.